注意
转到结尾下载完整的示例代码。
融合 Softmax¶
在本教程中,你将编写一个融合的 softmax 运算,对于特定类型的矩阵——即那些行可以放入 GPU SRAM 的矩阵——其速度明显快于 PyTorch 的原生算子。
通过本教程,您将了解到
核函数融合对于受带宽限制的操作所带来的好处。
Triton 中的归约运算符。
动机¶
用于逐元素加法的自定义 GPU 核函数在教学上很有价值,但在实践中作用不大。让我们转而考虑一个简单的(数值稳定的)softmax 运算的例子。
import torch
import triton
import triton.language as tl
from triton.runtime import driver
DEVICE = triton.runtime.driver.active.get_active_torch_device()
def is_hip():
return triton.runtime.driver.active.get_current_target().backend == "hip"
def is_cdna():
return is_hip() and triton.runtime.driver.active.get_current_target().arch in ('gfx940', 'gfx941', 'gfx942',
'gfx90a', 'gfx908')
def naive_softmax(x):
"""Compute row-wise softmax of X using native pytorch
We subtract the maximum element in order to avoid overflows. Softmax is invariant to
this shift.
"""
# read MN elements ; write M elements
x_max = x.max(dim=1)[0]
# read MN + M elements ; write MN elements
z = x - x_max[:, None]
# read MN elements ; write MN elements
numerator = torch.exp(z)
# read MN elements ; write M elements
denominator = numerator.sum(dim=1)
# read MN + M elements ; write MN elements
ret = numerator / denominator[:, None]
# in total: read 5MN + 2M elements ; wrote 3MN + 2M elements
return ret
当在 PyTorch 中简单实现时,对于 \(x \in R^{M \times N}\) 计算 y = naive_softmax(x) 需要从 DRAM 读取 \(5MN + 2M\) 个元素,并写回 \(3MN + 2M\) 个元素。这显然是浪费的;我们更希望有一个自定义的“融合”核函数,它只需读取一次 X 并在芯片上完成所有必要的计算。这样做只需要读取和写回 \(MN\) 字节,因此我们可以预期理论上约 4 倍的加速(即 \((8MN + 4M) / 2MN\))。torch.jit.script 标志旨在自动执行这种“核函数融合”,但正如我们稍后将看到的,它仍然远非理想。
计算内核¶
我们的 softmax 核函数工作原理如下:每个程序加载输入矩阵 X 的一组行(按程序数量进行跨步),对其进行归一化,然后将结果写回输出 Y。
请注意,Triton 的一个重要限制是每个块必须包含 2 的幂次方个元素,因此如果我们想要处理任何可能的输入形状,就需要对每一行进行内部“填充”,并适当地保护内存操作。
@triton.jit
def softmax_kernel(output_ptr, input_ptr, input_row_stride, output_row_stride, n_rows, n_cols, BLOCK_SIZE: tl.constexpr,
num_stages: tl.constexpr):
# starting row of the program
row_start = tl.program_id(0)
row_step = tl.num_programs(0)
for row_idx in tl.range(row_start, n_rows, row_step, num_stages=num_stages):
# The stride represents how much we need to increase the pointer to advance 1 row
row_start_ptr = input_ptr + row_idx * input_row_stride
# The block size is the next power of two greater than n_cols, so we can fit each
# row in a single block
col_offsets = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE)
input_ptrs = row_start_ptr + col_offsets
# Load the row into SRAM, using a mask since BLOCK_SIZE may be > than n_cols
mask = col_offsets < n_cols
row = tl.load(input_ptrs, mask=mask, other=-float('inf'))
# Subtract maximum for numerical stability
row_minus_max = row - tl.max(row, axis=0)
# Note that exponentiation in Triton is fast but approximate (i.e., think __expf in CUDA)
numerator = tl.exp(row_minus_max)
denominator = tl.sum(numerator, axis=0)
softmax_output = numerator / denominator
# Write back output to DRAM
output_row_start_ptr = output_ptr + row_idx * output_row_stride
output_ptrs = output_row_start_ptr + col_offsets
tl.store(output_ptrs, softmax_output, mask=mask)
我们可以创建一个辅助函数,为任何给定的输入张量将核函数及其(元)参数入队。
properties = driver.active.utils.get_device_properties(DEVICE.index)
NUM_SM = properties["multiprocessor_count"]
NUM_REGS = properties["max_num_regs"]
SIZE_SMEM = properties["max_shared_mem"]
WARP_SIZE = properties["warpSize"]
target = triton.runtime.driver.active.get_current_target()
kernels = {}
def softmax(x):
n_rows, n_cols = x.shape
# The block size of each loop iteration is the smallest power of two greater than the number of columns in `x`
BLOCK_SIZE = triton.next_power_of_2(n_cols)
# Another trick we can use is to ask the compiler to use more threads per row by
# increasing the number of warps (`num_warps`) over which each row is distributed.
# You will see in the next tutorial how to auto-tune this value in a more natural
# way so you don't have to come up with manual heuristics yourself.
num_warps = 8
# Number of software pipelining stages.
num_stages = 4 if SIZE_SMEM > 200000 else 2
# Allocate output
y = torch.empty_like(x)
# pre-compile kernel to get register usage and compute thread occupancy.
kernel = softmax_kernel.warmup(y, x, x.stride(0), y.stride(0), n_rows, n_cols, BLOCK_SIZE=BLOCK_SIZE,
num_stages=num_stages, num_warps=num_warps, grid=(1, ))
kernel._init_handles()
n_regs = kernel.n_regs
size_smem = kernel.metadata.shared
if is_hip():
# NUM_REGS represents the number of regular purpose registers. On CDNA architectures this is half of all registers available.
# However, this is not always the case. In most cases all registers can be used as regular purpose registers.
# ISA SECTION (3.6.4 for CDNA3)
# VGPRs are allocated out of two pools: regular VGPRs and accumulation VGPRs. Accumulation VGPRs are used
# with matrix VALU instructions, and can also be loaded directly from memory. A wave may have up to 512 total
# VGPRs, 256 of each type. When a wave has fewer than 512 total VGPRs, the number of each type is flexible - it is
# not required to be equal numbers of both types.
NUM_GPRS = NUM_REGS
if is_cdna():
NUM_GPRS = NUM_REGS * 2
# MAX_NUM_THREADS represents maximum number of resident threads per multi-processor.
# When we divide this number with WARP_SIZE we get maximum number of waves that can
# execute on a CU (multi-processor) in parallel.
MAX_NUM_THREADS = properties["max_threads_per_sm"]
max_num_waves = MAX_NUM_THREADS // WARP_SIZE
occupancy = min(NUM_GPRS // WARP_SIZE // n_regs, max_num_waves) // num_warps
else:
occupancy = NUM_REGS // (n_regs * WARP_SIZE * num_warps)
occupancy = min(occupancy, SIZE_SMEM // size_smem)
num_programs = NUM_SM * occupancy
num_programs = min(num_programs, n_rows)
# Create a number of persistent programs.
kernel[(num_programs, 1, 1)](y, x, x.stride(0), y.stride(0), n_rows, n_cols, BLOCK_SIZE, num_stages)
return y
单元测试¶
我们确保在一个具有不规则行数和列数的矩阵上测试我们的核函数。这将使我们能够验证我们的填充机制是否有效。
torch.manual_seed(0)
x = torch.randn(1823, 781, device=DEVICE)
y_triton = softmax(x)
y_torch = torch.softmax(x, axis=1)
assert torch.allclose(y_triton, y_torch), (y_triton, y_torch)
正如预期的那样,结果是相同的。
基准测试¶
在这里,我们将根据输入矩阵的列数来对我们的操作进行基准测试——假设有 4096 行。然后,我们会将其性能与 (1) torch.softmax 和 (2) 上面定义的 naive_softmax 进行比较。
@triton.testing.perf_report(
triton.testing.Benchmark(
x_names=['N'], # argument names to use as an x-axis for the plot
x_vals=[128 * i for i in range(2, 100)], # different possible values for `x_name`
line_arg='provider', # argument name whose value corresponds to a different line in the plot
line_vals=['triton', 'torch', 'naive_softmax'], # possible values for `line_arg``
line_names=["Triton", "Torch", "Naive Softmax"], # label name for the lines
styles=[('blue', '-'), ('green', '-'), ('red', '-')], # line styles
ylabel="GB/s", # label name for the y-axis
plot_name="softmax-performance", # name for the plot. Used also as a file name for saving the plot.
args={'M': 4096}, # values for function arguments not in `x_names` and `y_name`
))
def benchmark(M, N, provider):
x = torch.randn(M, N, device=DEVICE, dtype=torch.float32)
stream = getattr(torch, DEVICE.type).Stream()
getattr(torch, DEVICE.type).set_stream(stream)
if provider == 'torch':
ms = triton.testing.do_bench(lambda: torch.softmax(x, axis=-1))
if provider == 'triton':
ms = triton.testing.do_bench(lambda: softmax(x))
if provider == 'naive_softmax':
ms = triton.testing.do_bench(lambda: naive_softmax(x))
gbps = lambda ms: 2 * x.numel() * x.element_size() * 1e-9 / (ms * 1e-3)
return gbps(ms)
benchmark.run(show_plots=True, print_data=True)
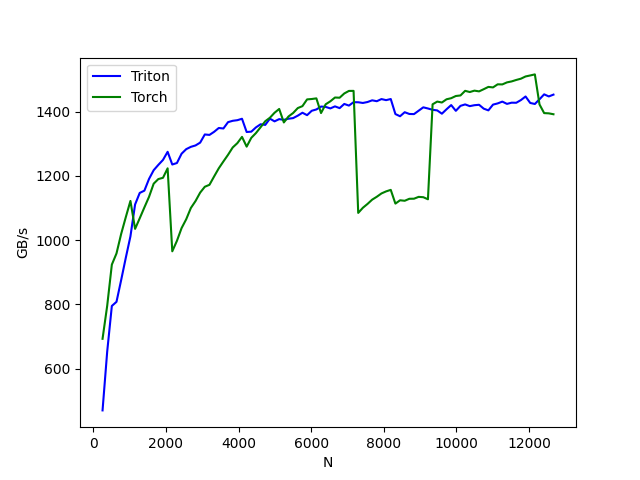
softmax-performance:
N Triton Torch Naive Softmax
0 256.0 473.659896 686.780756 207.861379
1 384.0 660.669287 806.008376 265.134838
2 512.0 815.158477 936.677599 304.872382
3 640.0 921.161345 918.350443 331.958893
4 768.0 991.315332 986.696988 350.987815
5 896.0 1046.260863 1028.174259 354.164124
6 1024.0 1078.125203 1075.766393 354.350425
7 1152.0 1100.917717 1078.684681 348.599930
8 1280.0 1126.358031 1110.405356 348.468866
9 1408.0 1168.753423 1137.744907 340.038040
10 1536.0 1197.438534 1160.772066 333.226260
11 1664.0 1209.427946 1191.943247 330.405439
12 1792.0 1229.164200 1194.767835 325.973656
13 1920.0 1254.596461 1226.943301 325.098761
14 2048.0 1273.114184 1250.854034 324.429271
15 2176.0 1235.791891 965.094258 325.554245
16 2304.0 1250.165402 1003.655589 325.991668
17 2432.0 1267.089432 1034.692550 326.615220
18 2560.0 1285.222170 1070.978154 328.089045
19 2688.0 1295.119487 1099.676083 329.180348
20 2816.0 1307.140929 1120.940049 328.973700
21 2944.0 1321.069707 1147.010745 331.637219
22 3072.0 1322.661110 1174.590823 333.500219
23 3200.0 1341.426737 1171.631122 335.257472
24 3328.0 1346.413514 1200.208687 336.082717
25 3456.0 1355.086561 1220.898055 337.155316
26 3584.0 1364.954471 1245.365855 337.824798
27 3712.0 1367.527564 1259.941993 340.448207
28 3840.0 1374.742348 1286.379219 340.600354
29 3968.0 1372.614562 1297.226640 340.639015
30 4096.0 1389.821524 1314.721360 338.627680
31 4224.0 1335.888625 1273.142024 343.270111
32 4352.0 1344.576962 1297.800717 345.450002
33 4480.0 1344.472079 1314.263422 346.171985
34 4608.0 1363.080836 1333.210600 347.225987
35 4736.0 1357.671200 1345.328302 347.902858
36 4864.0 1370.777009 1358.745694 349.349182
37 4992.0 1367.244211 1366.549965 350.349196
38 5120.0 1380.368035 1384.422157 350.665560
39 5248.0 1378.391261 1352.641992 351.658044
40 5376.0 1376.713540 1368.871166 351.327875
41 5504.0 1382.434889 1386.481428 353.871704
42 5632.0 1392.407944 1386.802310 353.155811
43 5760.0 1392.100296 1406.599945 354.670335
44 5888.0 1391.921935 1413.099426 354.781351
45 6016.0 1403.500755 1423.650071 356.694426
46 6144.0 1407.443367 1429.922661 356.778701
47 6272.0 1410.377175 1401.075033 357.585623
48 6400.0 1412.288505 1405.289253 358.345987
49 6528.0 1413.003402 1423.328624 359.093596
50 6656.0 1418.532837 1431.201285 359.016535
51 6784.0 1419.447719 1430.181966 360.192467
52 6912.0 1426.388130 1440.644841 360.537298
53 7040.0 1420.499466 1453.879176 361.048599
54 7168.0 1420.224596 1456.575759 361.942513
55 7296.0 1425.518507 1084.604309 362.611983
56 7424.0 1428.740100 1095.123650 362.853624
57 7552.0 1427.621187 1111.461079 363.655152
58 7680.0 1428.750077 1117.721214 363.500169
59 7808.0 1429.748227 1127.910759 363.985755
60 7936.0 1431.527695 1140.652897 364.759633
61 8064.0 1433.457794 1146.208664 364.664336
62 8192.0 1429.186574 1150.163399 364.335181
63 8320.0 1382.608906 1116.733384 362.080397
64 8448.0 1387.524387 1126.132973 362.715246
65 8576.0 1386.902266 1125.808072 363.822088
66 8704.0 1382.286100 1134.599626 364.534231
67 8832.0 1397.182562 1132.770862 365.156191
68 8960.0 1383.586312 1138.208823 365.785381
69 9088.0 1398.281650 1135.981204 366.227087
70 9216.0 1402.326434 1140.567790 367.307176
71 9344.0 1386.209007 1421.181611 367.595494
72 9472.0 1396.641195 1426.346139 368.824911
73 9600.0 1400.481225 1433.910037 368.915950
74 9728.0 1394.550970 1441.185199 369.772316
75 9856.0 1399.549850 1441.625982 370.320330
76 9984.0 1397.111341 1451.425485 370.671566
77 10112.0 1407.097007 1451.697726 371.455304
78 10240.0 1408.226767 1465.885411 371.604436
79 10368.0 1418.044835 1463.726121 369.779821
80 10496.0 1408.480147 1468.438786 370.284291
81 10624.0 1404.949970 1464.470314 371.015026
82 10752.0 1393.984629 1470.893384 370.714234
83 10880.0 1393.807467 1478.805877 371.886349
84 11008.0 1422.716118 1476.431579 372.540627
85 11136.0 1423.468600 1485.827556 372.832910
86 11264.0 1415.411657 1485.304111 373.094619
87 11392.0 1423.212828 1489.333603 374.593439
88 11520.0 1418.288448 1494.760803 373.794890
89 11648.0 1423.456893 1498.205001 374.724240
90 11776.0 1436.740864 1499.878597 374.753018
91 11904.0 1430.733250 1507.324669 375.236903
92 12032.0 1410.648275 1509.161423 376.389713
93 12160.0 1414.097640 1512.973901 375.917067
94 12288.0 1430.568382 1418.182569 375.972326
95 12416.0 1442.653252 1395.157695 375.176576
96 12544.0 1445.750558 1393.512648 375.428360
97 12672.0 1437.028767 1392.394033 375.242372
- 在上图中,我们可以看到
Triton 比 Torch JIT 快 4 倍。这证实了我们的怀疑,即 Torch JIT 在这里没有进行任何融合。
Triton 明显快于
torch.softmax——并且还**更易于阅读、理解和维护**。但请注意,PyTorch 的 softmax 操作更通用,可以处理任何形状的张量。
脚本总运行时间: (0 分 37.173 秒)